What is the Plastic Problem?
The consumption of plastic in India is increasing by a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10% every year. It is estimated that by 2020, India’s consumption of virgin plastics would reach a figure of about 20.0 Million Metric Tons (MMT) while recycled, plastics would be about 8.0 MMT. This prioritizes the importance of recycling and recovery of the plastic waste in the overall economy of plastics (ICPE, June 2017). The per capita consumption of plastic in India is 11 kgs per person, which is much below the world average per capita consumption of 28 kgs per person. The project is designed to address plastic waste recycling in a sustainable manner.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) India, in partnership with Hindustan Coca-Cola Beverages Private Limited (HCCBPL) is building on the existing systems and processes to reduce the impact of plastic waste on environment in India. The partnership is encouraging sustainable plastic waste management practices in India through collection, segregation and recycling of all plastics to move towards circular economy, which is in line with the Government of India's Swachh Bharat (Clean India) Mission, Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016 and Global Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
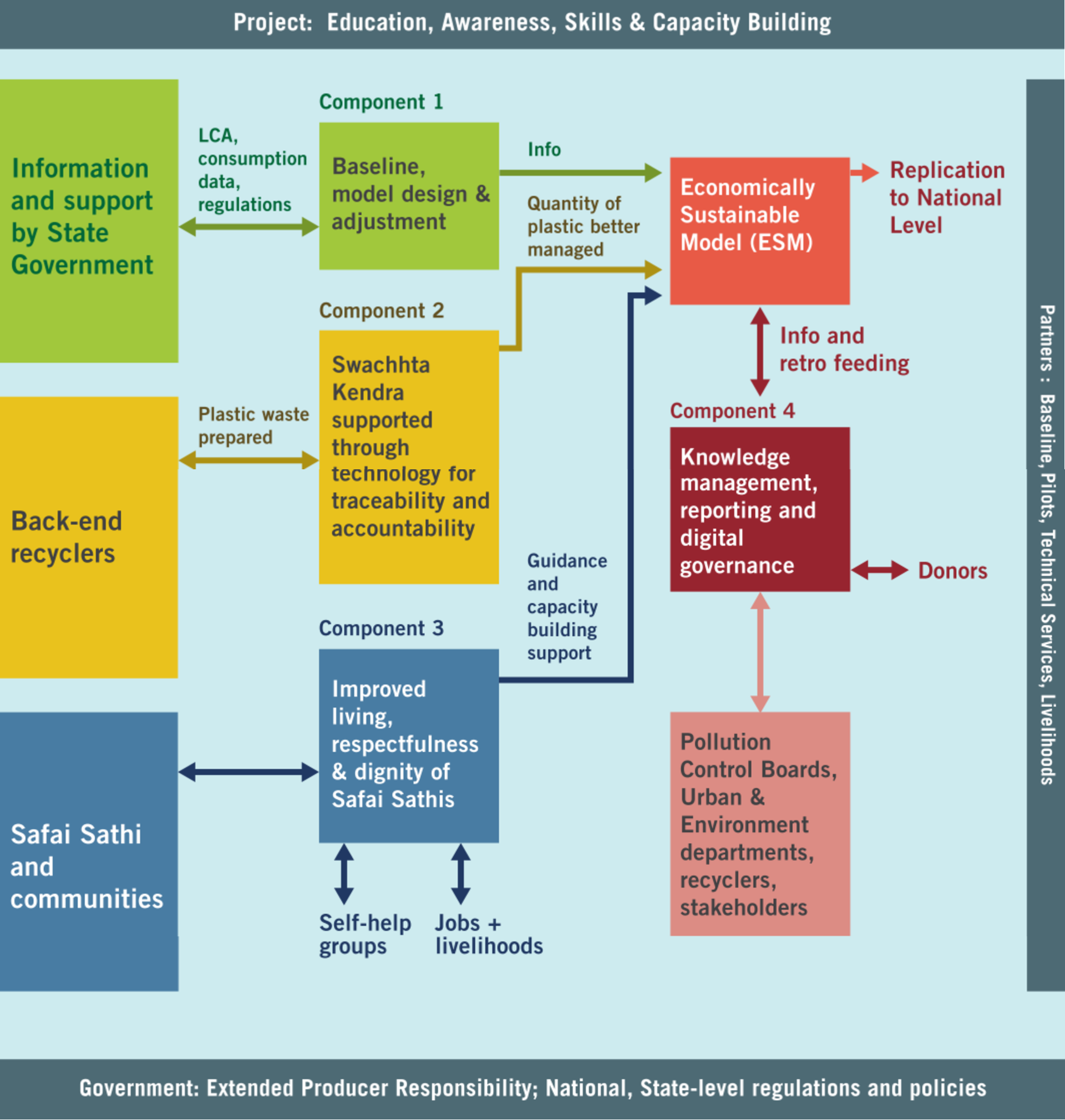
What We Aim To Do
Better manage more than 85,000 MT of plastic waste every year.
Improve the socio-economic conditions of 30,000 plus Safai Sathis (waste pickers).
Demonstrate a working model of Swachhta Kendras, blending social and technical approaches with strong governance mechanisms.
Institutionalize collaboration between citizen, communities, central and state pollution boards, urban and environment departments, related stakeholders to find sustainable solutions.
Our approach
Integrated Approach to Plastic Waste Management & Recycling